GATE 1996
Question 1 |
Let A and B be sets and let Ac and Bc denote the complements of the sets A and B. The set (A – B) ∪ (B - A) ∪ (A∩B) is equal to
A ∪ B | |
Ac ∪ Bc | |
A ∩ B | |
Ac ∩ Bc |
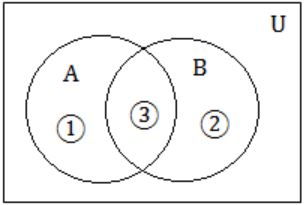
(A - B) = 1
(B - A) = 2
(A∩B) = 3
A∪B = (1∪2∪3)
(A – B) ∪ (B - A) ∪ (A∩B) = 1∪2∪3 = (A∪B)
Question 2 |
Let X = {2,3,6,12,24}, Let ≤ be the partial order defined by X ≤ Y if x divides y. Number of edge as in the Hasse diagram of (X,≤) is
3 | |
4 | |
9 | |
None of the above |
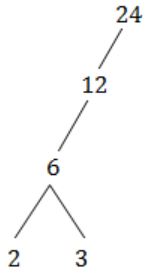
No. of edges = 4
Question 3 |
Suppose X and Y are sets and X Y and are their respective cardinalities. It is given that there are exactly 97 functions from X to Y. from this one can conclude that
|X| = 1, |Y| = 97 | |
|X| = 97, |Y| = 1 | |
|X| = 97, |Y| = 97 | |
None of the above |
|Y||X| = 97
→ Option A only satisfies.
Question 4 |
Which of the following statements is false?
The set of rational numbers is an abelian group under addition. | |
The set of integers in an abelian group under addition. | |
The set of rational numbers form an abelian group under multiplication. | |
The set of real numbers excluding zero in an abelian group under multiplication. |
Question 5 |
Two dice are thrown simultaneously. The probability that at least one of them will have 6 facing up is
1/36 | |
1/3 | |
25/36 | |
11/36 |
1 - (5/6 × 5/6) = 1 - (25/36) = 11/36
Question 6 |
The formula used to compute an approximation for the second derivative of a function f at a point X0 is
f(x0+h) + f(x0-h)/2 | |
f(x0+h) - f(x0-h)/2h | |
f(x0+h) + 2f(x0) + f(x0-h)/h2 | |
f(x0+h) - 2f(x0) + f(x0-h)/h2 |
f(x0+h) - 2f(x0) + f(x0-h)/h2
Question 7 |
Let Ax = b be a system of linear equations where A is an m × n matrix and b is a m × 1 column vector and X is a n × 1 column vector of unknowns. Which of the following is false?
The system has a solution if and only if, both A and the augmented matrix [A b] have the same rank.
| |
If m < n and b is the zero vector, then the system has infinitely many solutions. | |
If m = n and b is non-zero vector, then the system has a unique solution. | |
The system will have only a trivial solution when m = n, b is the zero vector and rank (A) = n. |
→ Solution can be depends on rank of matrix A and matrix [A B].
→ If rank[A] = rank[A B] then it can have solution otherwise no solution.
Question 8 |
Which two of the following four regular expressions are equivalent? (ε is the empty string).
- (i) (00)*(ε+0)
(ii) (00)*
(iii) 0*
(iv) 0(00)*
(i) and (ii) | |
(ii) and (iii) | |
(i) and (iii) | |
(iii) and (iv) |
In these two, we have any no. of 0's as well as null.
Question 9 |
Which of the following statements is false?
The Halting problem of Turing machines is undecidable. | |
Determining whether a context-free grammar is ambiguous is undecidbale. | |
Given two arbitrary context-free grammars G1 and G2 it is undecidable whether L(G1) = L(G2). | |
Given two regular grammars G1 and G2 it is undecidable whether L(G1) = L(G2). |
1) Membership
2) Emtiness
3) Finiteness
4) Equivalence
5) Ambiguity
6) Regularity
7) Everything
8) Disjointness
All are decidable for Regular languages.
→ First 3 for CFL.
→ Only 1st for CSL and REC.
→ None for RE.
Question 10 |
Let L ⊆ Σ* where Σ = {a, b}. Which of the following is true?
L = {x|x has an equal number of a's and b's } is regular | |
L = {anbn|n≥1} is regular | |
L = {x|x has more a's and b's} is regular | |
L = {ambn|m ≥ 1, n ≥ 1} is regular |
Here, m and n are independent.
So 'L' Is Regular.
Question 11 |
Which of the following is false?
 | |
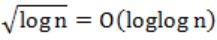 | |
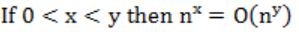 | |
 |

Question 12 |
Consider the following statements:
- (i) First-in-first out types of computations are efficiently supported by STACKS.
(ii) Implementing LISTS on linked lists is more efficient than implementing LISTS on an array for almost all the basic LIST operations.
(iii) Implementing QUEUES on a circular array is more efficient than implementing QUEUES on a linear array with two indices.
(iv) Last-in-first-out type of computations are efficiently supported by QUEUES.
Which of the following is correct?
(ii) and (iii) are true | |
(i) and (ii) are true | |
(iii) and (iv) are true | |
(ii) and (iv) are true |
(iv) LIFO computation efficiently supported by stacks.
Then given (i) and (iv) are false.
Answer:- A
Question 13 |
An advantage of chained hash table (external hashing) over the open addressing scheme is
Worst case complexity of search operations is less? | |
Space used is less | |
Deletion is easier | |
None of the above |
Question 14 |
In the balanced binary tree in the below figure, how many nodes will become unbalanced when a node is inserted as a child of the node “g”?

1 | |
3 | |
7 | |
8 |
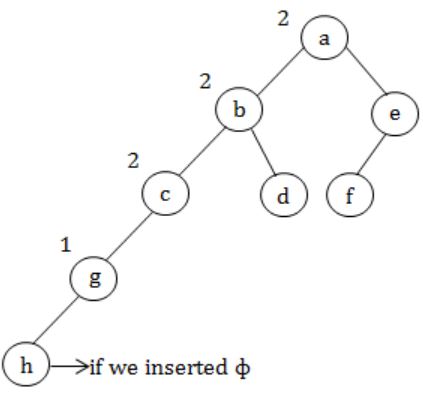
a, b, c are going to unbalance.
Question 15 |
Which of the following sequences denotes the post order traversal sequence of the tree of question 14?
f e g c d b a | |
g c b d a f e | |
g c d b f e a | |
f e d g c b a |
Left → Right → Root
g c d b f e a
Question 16 |
Relative mode of addressing is most relevant to writing
coroutines | |
position – independent code | |
shareable code | |
interrupt handlers |
Question 17 |
The pass number for each of the following activities
- 1. Object code generation
2. Literals added to literal table
3. Listing printed
4. Address resolution of local symbols
That occur in a two pass assembler respectively are
1, 2, 1, 2 | |
2, 1, 2, 1 | |
2, 1, 1, 2 | |
1, 2, 2, 2 |
Pass 1:
1) Assign addresses to all statements in the program.
2) Save the values assigned to all labels for use in pass 2.
3) Perform some processing of assembler directives.
Pass 2:
1) Assemble instructions.
2) Generate data values defined by BYTE, WORD etc.
3) Perform processing of assembler directives not done during pass 1.
4) Write the program and assembling listing.
Question 18 |
The process state transition diagram in below figure is representative of

a batch operating system | |
an operating system with a preemptive scheduler | |
an operating system with a non-preemptive scheduler | |
a uni-programmed operating system |
So this is preemptive.
